Following the series “Quantum Logic Gates”, let’s talk today about the most intuitive of all quantum gates, the quantum logic gate created by Wolfgang Pauli that has his name. There are 3 kinds of them: Pauli X, Pauli Y and Pauli Z.
 Wolfgang Pauli, creator of Pauli’s matrix
Wolfgang Pauli, creator of Pauli’s matrix
Pauli X Gate or NOT Gate
In essence, the quantum logic gate NOT, also known as Pauli X gate acts identical to the classic logic gate NOT. As we can see in the diagram below, two inputs, with their respective values of A|0> and B|1>, have their outputs inverted, going to A|1> and B|0>.

This gate, which acts on only a single Qubit, has the diagram below used to represent it in a quantum circuit. The actuation of this gate is equivalent to a rotation of 180º, or π radians, on the x axis of the Bloch sphere, which is a representation for Qubits that we have already covered in this post and in this one as well.
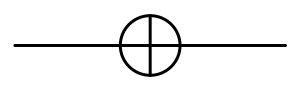
In short, the quantum logic gate NOT or Pauli-X gate, inverts the logical value of an input |0> to |1>, and an Input |1> to |0>. It receives this “Pauli X gate” name, on account of the matrix used to represent it, which is the matrix of Pauli:
The author of the bible of Quantum Computation, “Quantum Computation and Quantum Information”, Michael A. Nielsen, released a video on youtube telling us a little more about this logical gate, as we can see below:
Pauli Y Gate
The quantum logic gate Pauli Y, acts on a single Qubit. The actuation of this gate is equivalent to a rotation of 180º, or π radians, on the y-axis of the Bloch sphere, transforming a value of |0> to i|1> and a value of |1> to –i|0>. It receives the name of Pauli Y gate, by the matrix of Pauli that represents it:
It is drawn with the following diagram, in the quantum circuits:
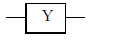
In this video below, we can see around 25 seconds the action of the Pauli Y gate in a Bloch sphere:
Pauli Z gate
Just like its sisters, Pauli Y and Pauli X, this gate acts on a single Qubit. The actuation of this gate is equivalent to a rotation of 180º, or π radians, in the Z axis of the Bloch sphere. It maintains the initial state |0> unchanged and maps |1> to -|1>. Because of its nature, it is also called a phase-flip gate / phase-shift gate, a special case of this quantum gate category. It receives the name of Pauli Z gate, because of the Pauli matrix that represents it:
It is drawn with the following diagram, in the quantum circuits:

In this video below, we can see around 28 seconds the action of the Pauli Z port in a Bloch sphere:
That’s all for now folks! Next week we will talk about Fredkin and Toffoli gates.
Reference:
Série: Portas lógicas quânticas 2 – NOT gate
Série: Portas lógicas quânticas 3 – Pauli Y gate
Série: Portas lógicas quânticas 4 – Pauli Z gate




 Integrated Circuit
Integrated Circuit
 Jon Schiller Book
Jon Schiller Book Seth Lloyd’s Book
Seth Lloyd’s Book A big Quantum Computer named universe
A big Quantum Computer named universe Earth = MC²?
Earth = MC²? Quantum Mine Gold
Quantum Mine Gold